- News & Insights
- 2025
- What if Packaging Never Became Waste? The Power of Circular Engineering
What if Packaging Never Became Waste? The Power of Circular Engineering
The global packaging waste crisis is becoming increasingly urgent.
In the United States alone, an estimated 96 million tons of packaging waste are generated annually, according to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)1. Meanwhile, the European Union produced around 83.4 million tons of packaging waste in 20222. In Southeast Asia, plastic pollution is also a significant concern, with over 31 million tons of plastic waste generated yearly across six of the ten ASEAN countries3.
This rising waste crisis has spurred governments, businesses, and consumers to demand more sustainable packaging solutions. Stricter environmental regulations worldwide are pushing industries to rethink their packaging strategies, leading to the rapid adoption of circular engineering principles. As businesses face growing pressure to adopt responsible packaging solutions, circular engineering offers a structured approach to resource efficiency, waste reduction, and sustainable materials innovation.
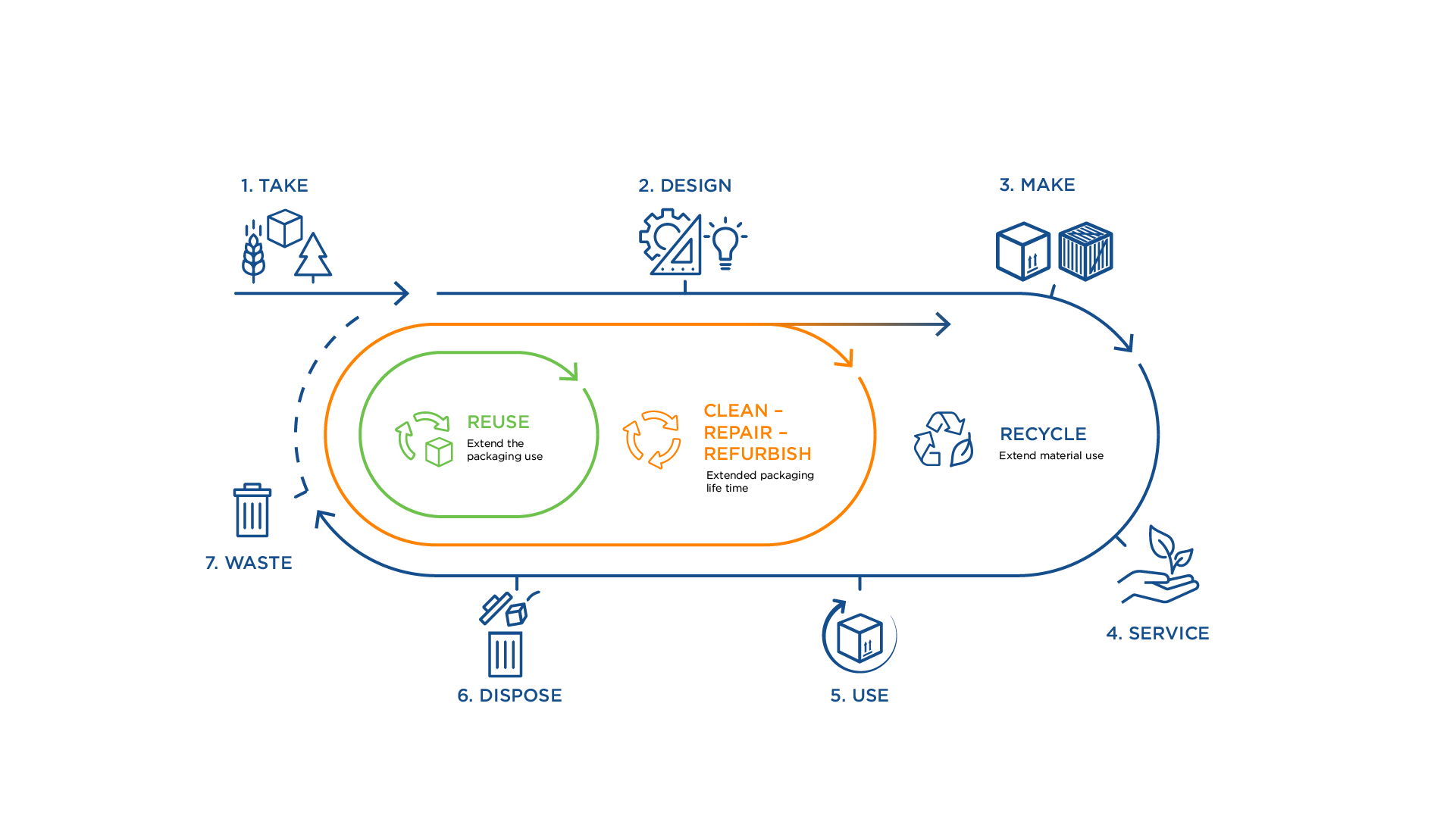
Circular Engineering replaces the “take-make-waste" model with a system that keeps resources in circulation longe through reuse, repair and recycling.
What is Circular Engineering?
Green engineering focuses on creating industrial processes that are both economically viable and environmentally responsible, reducing harm to people and the planet4. Circular engineering builds upon this by transforming how we perceive and use resources. Rather than treating materials as disposable, it views them as valuable assets to be preserved5.
Instead of just managing waste, circular engineering prevents it from being created in the first place by extending the life of materials through reuse, recycling, and smarter design. Unlike traditional packaging engineering, which prioritizes cost and functionality, sustainable engineering integrates environmentally conscious principles at every stage—from design to disposal. It moves away from the outdated “take-make-waste" model to a system that keeps resources in circulation longer, tackling resource scarcity, waste management, and climate change, and making sustainability a core principle of modern engineering6.
The circular economy could generate $4.5 trillion in global economic benefits by 2030, according to the World Economic Forum.
(https://www.weforum.org/impact/helping-the-circular-economy-become-a-reality/)Circular Engineering in Packaging Design
Packaging engineers are rethinking design to make packaging more sustainable—reducing waste while still protecting products and keeping costs in check. By applying circular principles, they are shifting away from single-use materials and finding smarter ways to keep packaging in circulation.
From choosing better materials to redesigning packaging for easy recycling and creating reusable systems, companies are finding innovative ways to make circular packaging work. Here’s how these strategies are bringing sustainability to life.
Smart Material Selection
A major shift is occurring in material selection, with a focus on reducing waste while ensuring optimal product protection. Companies are designing packaging with circularity in mind, meaning materials are chosen to stay in use longer and reduce environmental impact. Sustainable packaging solutions now:
- Work with existing recycling system, making disposal easier
- Are made with post-consumer recycled (PCR) materials, cutting down on the need for virgin resources
- Offer strong, reliable protection while using fewer raw materials.
From recyclable plastics to fiber-based alternatives, businesses are investing in materials thatalign with circular engineering principles—helping to create a packaging system that’s bothsustainable and efficient.
Innovative Packaging Design Strategies
Preventing waste begins at the design stage. Packaging engineers now focuses on:
- Designing for easy separation: ensuring that packaging components can be effortlessly separated for recycling.
- Reducing material use: optimizing designs to use only the necessary amount of material.
- Rigorous testing: designing lightweight packaging that maintains strength and functionality through scientific testing.
Optimized packaging solutions use fewer materials, reduce waste, lower transportation costs, and improve storage efficiency, making them both environmentally and economically beneficial.
Closed-Loop Business Models for Circular Packaging
Sustainability isn't just about materials—it’s about rethinking how packaging is used, reused and recovered. Circular engineering strategies are transforming business models to keep packaging in circulation longer, reducing waste and improving efficiency:
- Shared packaging systems: packaging materials are repaired and reused, such as pooling services for transport packaging.
- Reusable solutions: designed for multiple-use cycles to minimize waste and extend life.
- Material repurposing: closing the loop by transforming waste into reusable raw materials.
- Reverse logistics and take-back programs: ensuring packaging is returned for reuse, repair or recycling, rather than becoming the waste.
According to report7 by the Ellen McArthur Foundation, replacing just 20% of single-use plastic packaging with reusable alternatives could unlock $10 billion in economic opportunities worldwide.

The Role of Packaging Engineers in Sustainability
Packaging engineers are at the forefront of integrating circular engineering into sustainable solutions and collaboration across industries is essential to drive meaningful change. Their role includes:
- Developing new materials and packaging designs: engineers are leading the development of novel materials and designs that optimize recyclability and resource efficiency.
- Collaborating with supply chain partners: sustainable packaging requires close collaboration with suppliers, manufacturers, and recyclers to ensure a holistic approach.
- Conducting Life Cycle Assessments (LCA) to ensure compliance with environmental standards.
According to a report from impact organization Circle Economy, circular strategies have the potential to reduce global greenhouse gas emissions by 39%, making them a key solution in preventing climate breakdown.
Industry Collaboration for Sustainable Engineering
Sustainability is a shared responsibility, and real progress comes from collaboration. Recognizing this, Nefab has established Packaging Engineers for a Sustainable Future—a community of passionate engineers, including customers, vendors, former employees, and university alumni, all committed to advancing technical and sustainable innovations.
"Engineering is the backbone of the circular economy. As packaging engineers, our mission goes beyond minimize waste – we must redefine how materials are used, integrating more recyclable and reusable solutions wherever possible. Through Packaging Engineers for a Sustainable Future, we are building a space for knowledge-sharing, collaboration, and innovation. Everyone is encouraged to contribute, exchange ideas, and work together to drive real change. The future of sustainable packaging starts with us so let’s lead the way." - David Nowak, Nefab’s Global Engineering Director.
We save resources in supply chains for a better tomorrow.
Want to learn more?
GET IN TOUCH
Contact us to learn more about our smart and sustainable solutions.
LEARN MORE
Sustainable Solutions
Engineered packaging for sustainable supply chains
GreenCalc
Nefab’s own certified calculator measures and quantifies financial and environmental savings in our solutions
Global Engineering Network
250 engineering experts in more than 30 locations

